Skip links allow screen readers, keyboard users, and other assistive technology users to quickly navigate to the main content and skip over large headers or navigation. In this article, I’ve explained the need for skip links, how skip links improve accessibility, and the steps to build a skip link.
1. Understanding the Problem 💻
Nowadays websites have large headers or navigation. This makes it difficult for screen reader and keyboard users to quickly navigate to the main content. They need to tab through each navigation link before reaching the main content. This results in a bad user experience.
2. Skip Links: The Solution 🔗
To make it easy for screen readers, keyboard users, and other assistive technology users to navigate to the main content, skip links should be built.
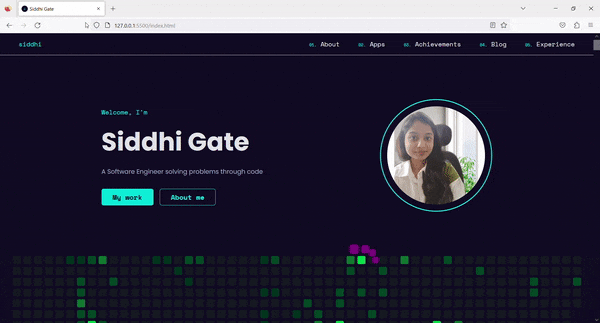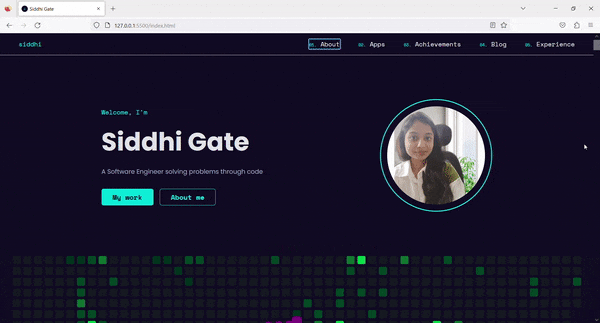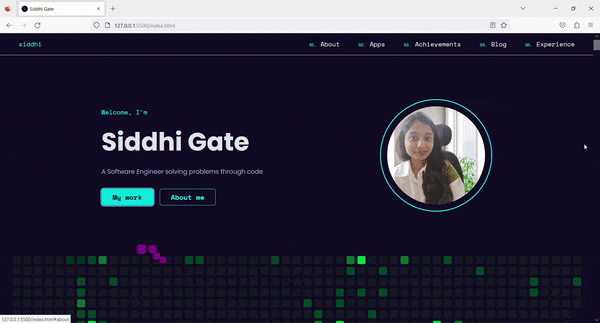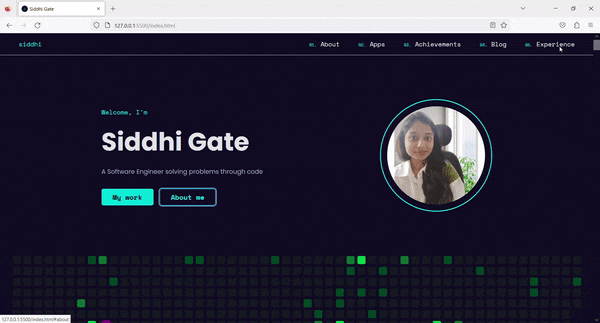
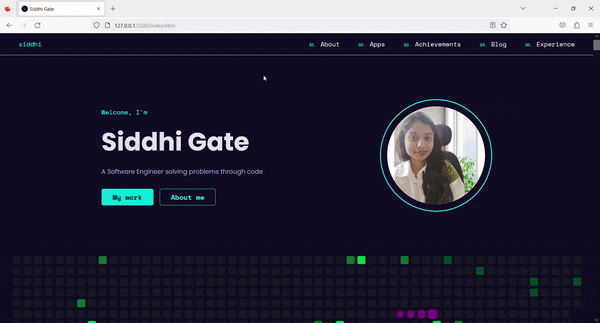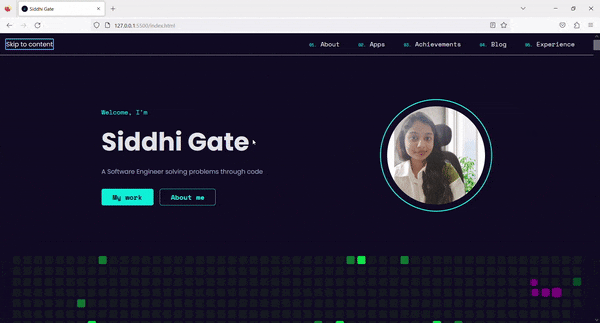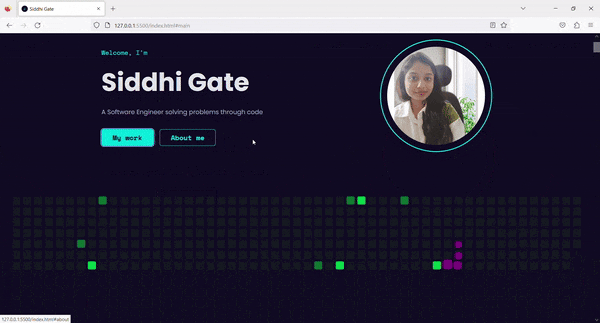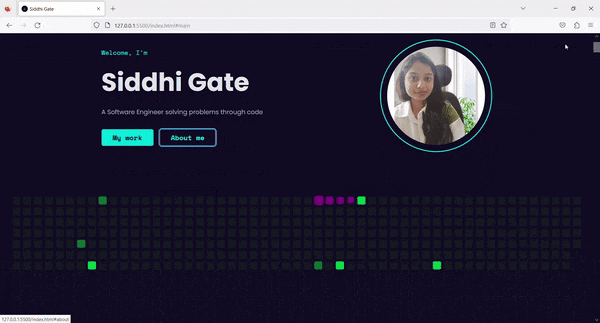
Skip links are present at the top of the website and are visually hidden.
On the first
Tabpress, this link gains focus and is visible to the users.The users can then navigate directly to the main content by using the link.
3. Building a Skip Link 👩💻
Following are the steps to build a skip link:
Create a link that navigates it to the main content.
Place the link at the top of the website so that it gains focus on the first
Tabpress.Make the link visually hidden.
Show the link on focus.
3.0 The basic setup
The body of the HTML has 4 navigation links and then the main content. Screen readers or keyboard users will travel through all these navigation links before going to the main content.
<body>
<nav>
<a href="/">Nav link 1</a>
<a href="/">Nav link 2</a>
<a href="/">Nav link 3</a>
<a href="/">Nav link 4</a>
</nav>
<main>
<h1 id="main">Hello world </h1>
<a href="/">About us</a>
</main>
</body>
3.1. Creating a link
Create a link to the main content on the page.
Place it at the top of the web page.
<body>
<a href="#main" class="skip-link">Skip to content</a>
<nav>
<a href="/">Nav link 1</a>
<a href="/">Nav link 2</a>
<a href="/">Nav link 3</a>
<a href="/">Nav link 4</a>
</nav>
<main id="main">
<h1>Hello world </h1>
<a href="/">About us</a>
</main>
</body>
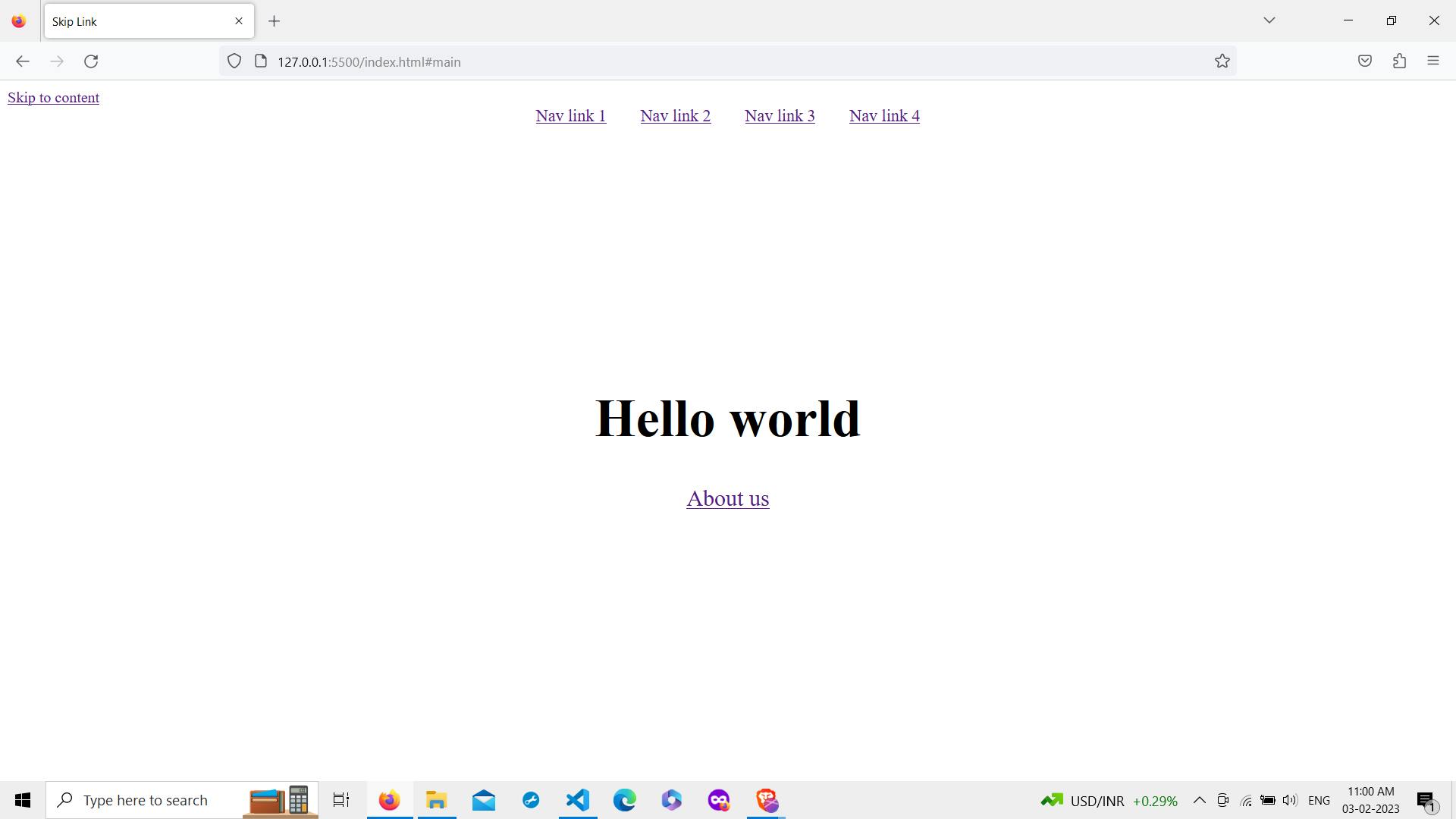
3.2. Hiding the link
Giving the link an absolute position and translating it by the X-axis by -100% will make it hidden.
.skip-link {
position: absolute;
background: white;
transform: translateX(-100%);
overflow: hidden;
width: 1px;
}
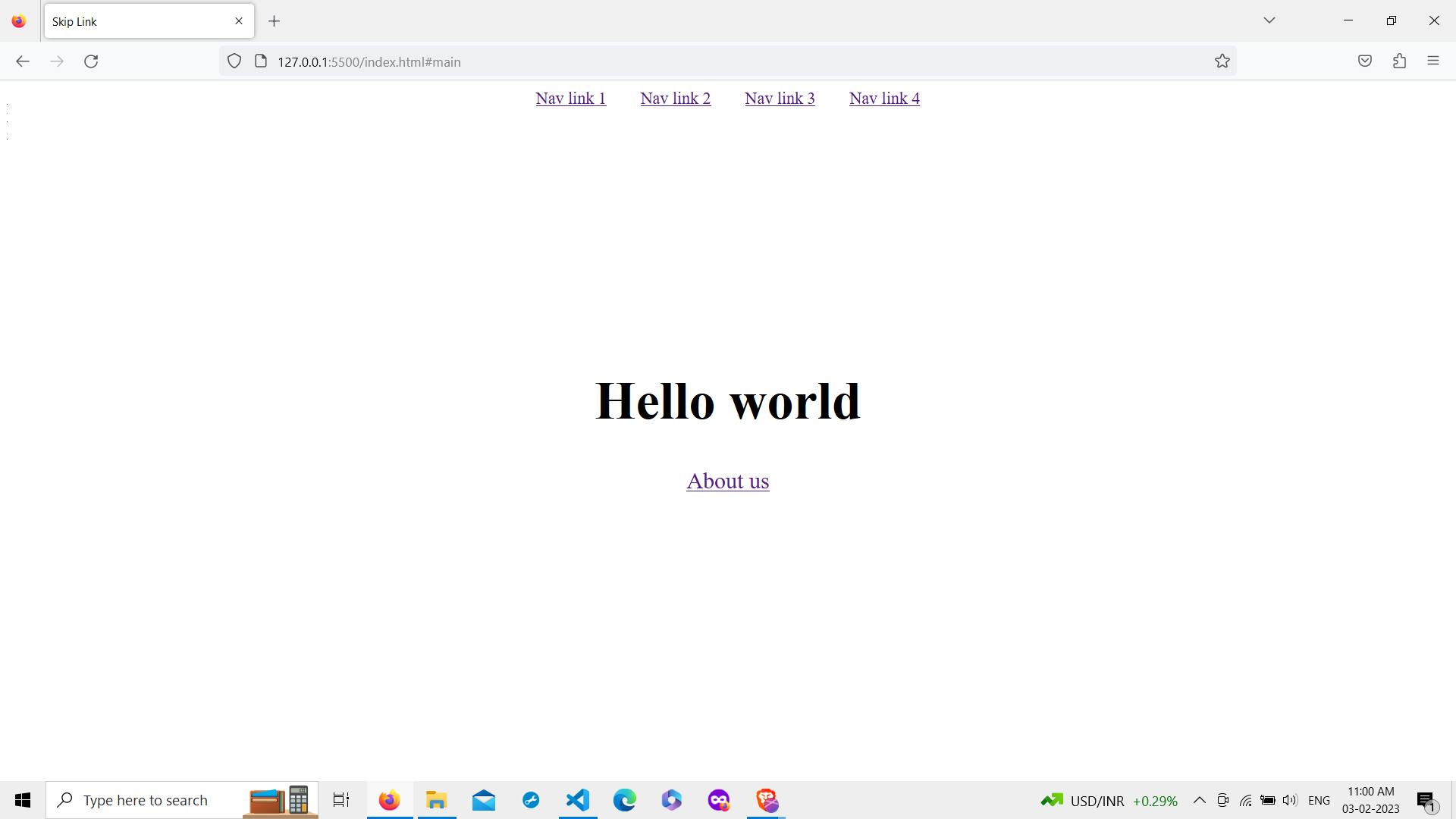
3.3. Showing the link on focus
Translating the skip link to 0% will make the link visible.
.skip-link:focus {
transform: translateX(0%);
overflow: auto;
width: auto;
}

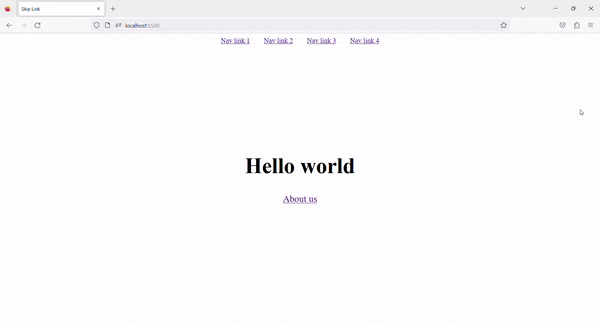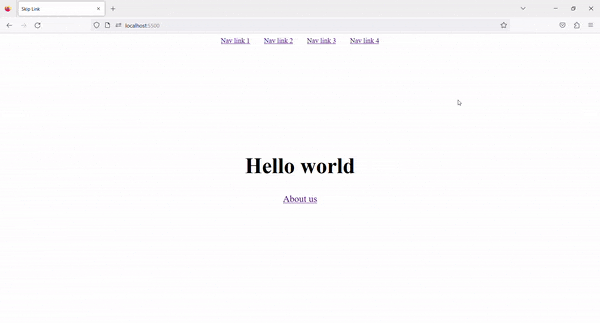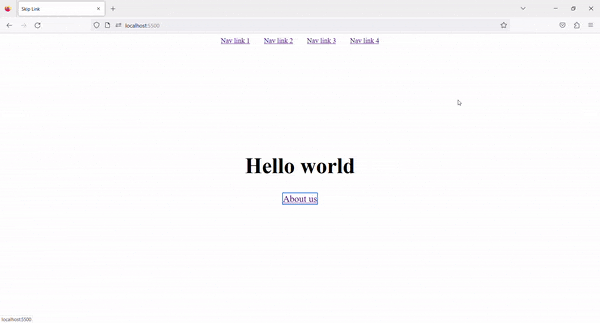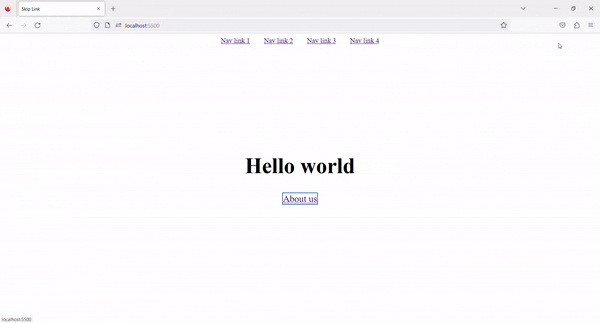
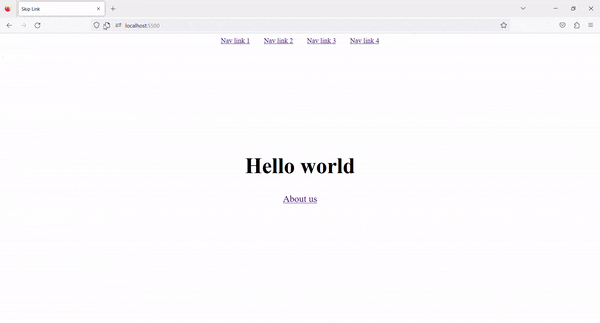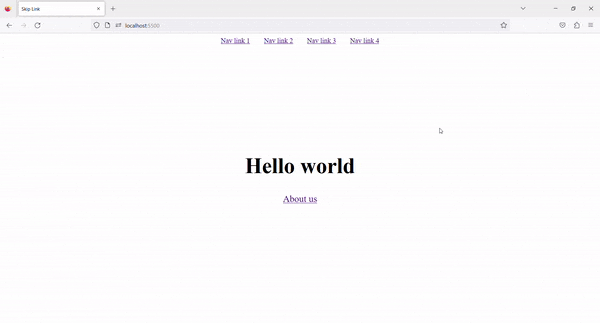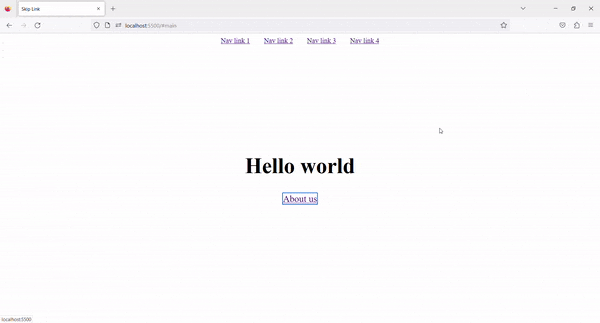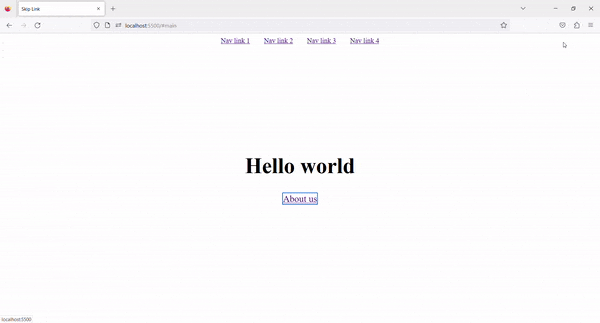
4. Result ✨
Now, on Tab press, the Skip to content link is visible. By clicking on that link, we can skip the navigation links and go directly to the main content.
5. That’s all folks 🙌
By providing a quick and easy way for users to navigate directly to the main content, skip links can improve the overall user experience and accessibility of a website.
Let’s connect:
